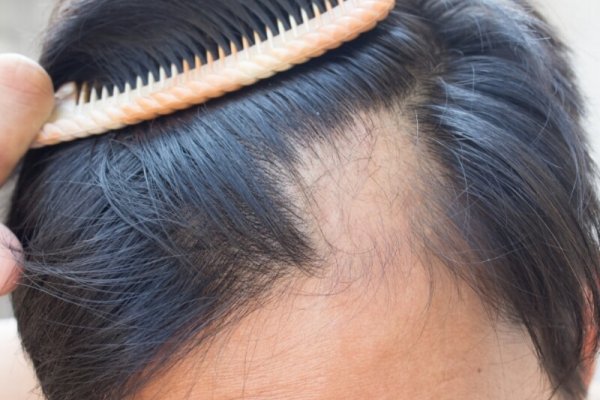
Hair Loss
Many people, of all ages and genders, experience increased hair loss or varying degrees of thinning (androgenetic alopecia) or suffer from diseases of the hair and scalp, leading to alteration of the stem or complete atrophy of the scalp. hair follicle.
What is hair loss?
Hair loss is a symptom of a large group of diseases and requires specialization for its correct diagnosis and effective treatment. Proper and timely diagnosis is of particular importance, as it is often the underlying disease that needs immediate treatment, and not just the symptom of hair loss. All patients have a detailed personal and family history taken and we discuss their health status and possible diseases of other organs that may affect hair growth.
Personalized Valuation of Hair Loss
The evaluation is detailed in order to identify the various factors that contribute to the development of the problem in each person. In every patient, personal and family history is recorded in detail as well as the state of health and possible diseases of other organs that may affect hair growth are discussed.
If necessary, certain general biochemical haematological tests are performed to detect possible disorders (anemias, hormonal abnormalities, etc.) or to detect vitamins, trace elements, amino acids or other factors, such as microorganisms (e.g. Candida), which affect the hair as a whole or individually.
This is followed by examination of the scalp skin and hair with dermatoscopy, trichorizogram, examination of the hair with polarized light or other methods, and biopsy, when required.
Causes of Hair Loss
Androgenetic alopecia causes thinning of the hair, with or without an increase in hair loss. This phenomenon is due to a time reduction of the growth phase or regenerative phase of the hair life cycle. This reduction causes shrinkage of the hair follicles, which leads to shorter and thinner hairs.
Research has shown that there is increased hair loss in the fall compared to other seasons. This increase in hair loss is due to the fact that an increased number of hairs enter the resting phase or otherwise the telogen phase of their life cycle in July. This stage takes place about 100 days before hair loss. This variation in the rate of hair loss may be due to an evolutionary advantage, with hair falling out only after keeping the scalp warm in winter and after protecting it from the sun during the summer.
This should not cause any concern and is perfectly normal. This white bulb is the part of the hair that is closest to its root. This means that the hair fell from its base and did not break along its axis. These hairs are in the resting phase or in the telogen phase of the hair cycle and it is normal for them to fall out.
Stress could be one of the factors that causes hair loss. Increased stress leads to increased cortisol production, which negatively affects the function and regulation of the hair cycle. This reaction can lead to hair loss under stress.
Telogen effluvium is an example of a pathophysiological process that leads to hair loss due to physical or mental stress. In addition, psychological stress can lead to premature graying of hair.
Male or female type alopecia (baldness) is the most common cause of hair loss. This condition is also known as “androgenic alopecia” because hair loss is caused by two main factors: androgens (male hormones) and genetic predisposition.
Androgen production increases after the onset of puberty. Therefore, the first obvious signs of androgenetic alopecia usually begin in adolescence. The most important hormone for the development of this form of hair loss is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is a very powerful androgen. DHT is produced locally in the hair follicle by testosterone conversion. The conversion of testosterone to DHT is regulated by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme is the target of the drugs used to treat hair loss and are called finasteride and dutasteride. Pockets predisposed to androgenetic alopecia produce larger amounts of DHT, compared to pockets that do not have such a predisposition.
Baldness is inherited, but the exact genes that predispose to baldness are unknown. We know that baldness is polygenic, which means that it is affected by many different genes. It is impossible to know for sure whether a person will develop baldness based on the presence of baldness in specific blood relatives. However, increasing the number of bald family members puts one at higher risk. Higher hereditary predisposition puts one at increased risk of developing severe baldness at a young age.
We could summarize by saying that many genes from both father and mother affect hair growth. Men are more influenced, not exclusively, by their mother’s family and women by their father’s family. Therefore, prognosis should be seen, respectively, the male members of the mother’s family for men and the female members of the father’s family for women.
Androgenic alopecia only affects certain areas of the scalp called “androgen-dependent areas”. These are areas that have high levels of androgen hormone receptors in the cells of the hair follicles and are therefore particularly prone to baldness. These areas are located on the front of the hairline and on the top of the head.
Some areas of the scalp are resistant to androgenetic alopecia and do not lose hair even in cases of severe baldness, ie the occipital region and peripheral to the scalp. These areas are used by hair transplant surgeons to collect hair follicles.
We do not have the ability to cure androgenic alopecia, but treatment can stop the progression, promote hair growth and thicken the tiny hair follicles.
Hair transplantation can achieve excellent aesthetic results in many of the patients.
A vegetarian or homophagous diet includes the possibility of insufficient iron intake. Iron deficiency can have a number of negative effects on health, including hair. You can take an iron supplement, or eat foods rich in iron to make sure your diet contains enough iron. Foods rich in iron are spinach, lentils, quinoa and broccoli.
Lysine supplements can help improve iron absorption. Ask your doctor to assess the levels of iron in your body, in case you think it may be insufficient.
Yes, your thyroid can be the cause of hair loss. Thyroid function (TSH, T3, T4) is always monitored in patients suffering from hair loss. Telogen effluvium is for example one of the types of hair loss that can be caused by a thyroid dysfunction.
Hypothyroidism can also lead to dull, brittle hair. Before taking the above tests, tell your doctor if you are taking a biotin supplement.
Biotin may affect the results of these tests and you may be required to stop taking biotin for about 2 days before the day of the test.
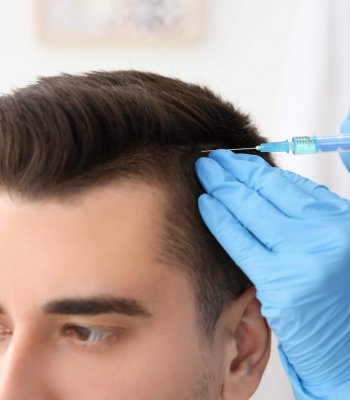
Hair loss treatments
This comprehensive examination and the data collected lead to the selection of personalized therapeutic methods, which include:
- the topical application of minoxidil and other drugs and growth factors (PRP etc.), in densities and combinations prepared specifically for each person,
- the introduction of these preparations deeper into the hair follicles by iontophoresis, without pain or by local injection,
- the autologous mesotherapy with platelet rich plasma (PRP), which includes growth factors and the concomitant oral administration of trace elements and amino acids used by the hair to grow,
- the administration of oral drugs with local action on the hair follicles without side effects,
- the use of lasers and other types of phototherapy, which can be applied even at home and also
- hair transplantation by all methods. The two oldest methods are FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction).
In FUT, a strip of hairy skin is removed from the occipital region (donor area), which is properly prepared and implanted in the parietal and frontal area of the head, while in FUE, a hair follicle is removed one by one and implanted in areas with fewer and thinner hairs. However, small scars remain when the hairs are removed from the donor area.
Exclusive PL-FUT transplant method
According to a newer hair transplant method called PL-FUT, half of the hair follicle is taken from the donor area and is implanted in the front area of the head. Thus, from the two “half” hairs, front and back, the whole hairs are regenerated. In this way, the donor area is protected, without the development of visible scars.
The results are monitored with special computer evaluation machines.
Our Contacts
Contact us!
Agias Sofias 28, Thessaloniki
info@dermaesthetichair.gr
(+30) 2310 282.292 & 2310 250.300

